Posterior View of the Intracranial Aspect of the Left Jugular Foramen
6014
Surgical Correlation
Tags
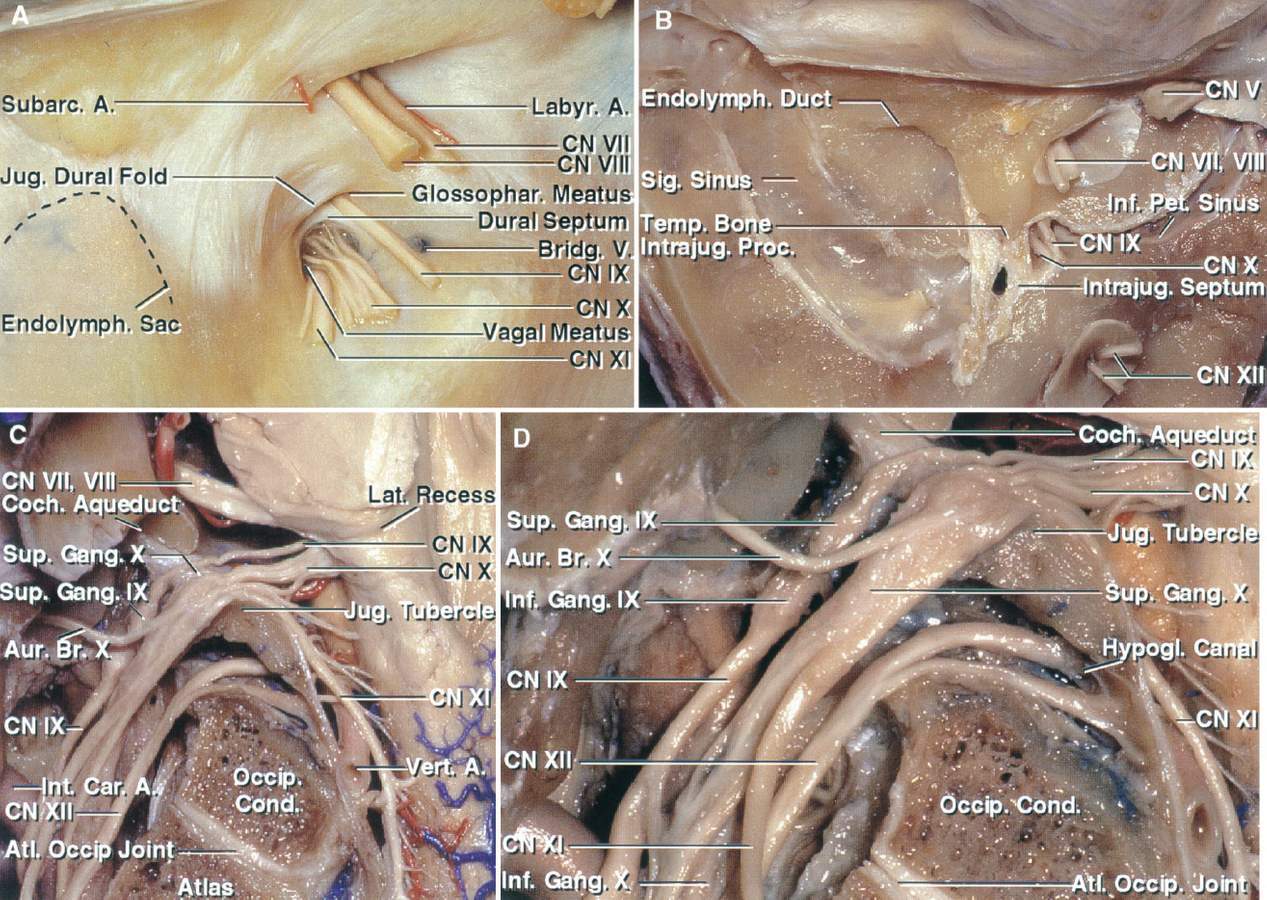
A, Posterior view of the intracranial aspect of the left jugular foramen. The glossopharyngeal, vagus, and accessory nerves pierce the dural roof of the jugular foramen. The glossopharyngeal nerve is separated from the vagus nerve by a narrow dural septum. The jugular dural fold projects downward and medially from the lateral and upper margin of the jugular foramen over the site at which the nerves enter the dura roof of the foramen. The facial and vestibulocochlear nerves and labyrinthine artery enter the internal acoustic meatus. The subarcuate branch of the anteroinferior cerebellar artery enters the subarcuate fossa. The endolymphatic sac is located between the dural layers lateral to the jugular foramen. A bridging vein from the medulla joins the inferior petrosal sinus on the medial side of the jugular bulb. B, The dura has been removed from the posterior surface of the temporal bone. The intrajugular processes of the temporal and occipital bones, which are connected by a fibrous bridge, the intrajugular septum, separates the sigmoid and petrosal parts of the foramen. The glossopharyngeal, vagus, and accessory nerves enter the intrajugular part of the foramen by penetrating the dura on the medial side of the intrajugular process of the temporal bone. C, The glossopharyngeal nerve enters the jugular foramen below the cochlear aqueduct. The vagus nerve enters the jugular foramen behind the glossopharyngeal nerve. The auricular branch of the vagus nerve (Arnold’s nerve) arises at the level of the superior ganglion and passes around the anterior wall of the jugular bulb. The accessory nerve is formed by multiple rootlets, which arise from the medulla and spinal cord. The accessory rootlets collect together to form a bundle that blends into the lower margin of the vagus nerve at the level of the jugular foramen. The lower vagal and accessory roots pass across the surface of the jugular tubercle. D, Enlarged view. The glossopharyngeal nerve expands at the site of the superior and inferior ganglia. The superior ganglion of the vagus nerve is located at the level of or just below the dural roof of the foramen, and the inferior ganglion is located below the foramen at the level of the atlanto-occipital joint. (Images courtesy of AL Rhoton, Jr.)